
- Home
- 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance
- Electronic Batch Records for Digital Pharmaceutical Compliance
21 CFR Part 11 Compliance

Electronic Batch Records for Digital Pharmaceutical Compliance
Electronic Batch Record | EBR | Batch Manufacturing Record | BMR | Good Manufacturing Practices | GMP
This white paper is about Electronic Batch Records (EBR) and the role they play in creating a fully digital pharmaceutical manufacturing environment that complies with 21 CFR Part 11.
For many years pharmaceutical manufacturing companies have produced drugs, medicines, and therapeutics in large batches to control the economics of the final product. Producing large batches enables the manufacturer to keep tight control over the product formulation process with control over quantities and processes.
Batch Manufacturing Records (commonly known as EBR’s) have been the backbone of lot and batch traceability for pharmaceutical companies for decades and have been a vital part of the manufacturing due diligence process to meet strict regulatory standards.
This document explains the basics of formulation processes and how batch records are utilized by pharmaceutical manufacturers to create a paperless and credible traceability process that stands up to the pharmaceutical regulations.
What is a Batch Manufacturing Record (BMR)?
After a batch has been formulated in production (often a combination of weighed, bagged, and bulk ingredients), all the steps will need to be documented. A Batch Manufacturing Record (BMR) provides the documentation which lists out, step by step the ingredient quantities added to the batch. Extra data such as dates added, supplier and internal lot codes, the operator responsible, date & time, location, etc.
All the data captured provides the manufacturer with batch traceability in addition to proving Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) have been adhered to. GMP requirements include formulation sequences, standard operating procedures, mixing instructions, and basically anything that’s pertinent to showing that the operator has followed a structured batch manufacturing process.
There is an enormous amount of variability in drug manufacturing processes which is largely centered around the manufacturing batch size (all of which should be detailed within an electronic batch record (EBR) – see section below). Many manufacturers rely on hand weighing using small precision balances for the active ingredients while using heavy capacity weighing equipment / PLC controlled bulk handling equipment for the less critical ingredients. The equipment used during the process is almost entirely driven by the desired batch size.
Obviously, the more complex the manufacturing process, the more challenging the Batch Manufacturing Record keeping process becomes. This complexity has created a need for more automation and less room for error in manufacturing.
Manual Batch Manufacturing Records are still very common today (to demonstrate Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in addition to verified traceability), but their credibility can be suspect and expensive to produce – often requiring supervisors to watch and document a batch process that is already being recorded by a batch production operator. This cost has created an opportunity for fully electronic batch records, known as EBR’s.
What is an Electronic Batch Records (EBR)?
Batch manufacturing processes can be complex, time-consuming, and lengthy. Pharmaceutical manufacturers are now implementing computerized systems to provide automatically generated Electronic Batch Records, or EBR’s for short.
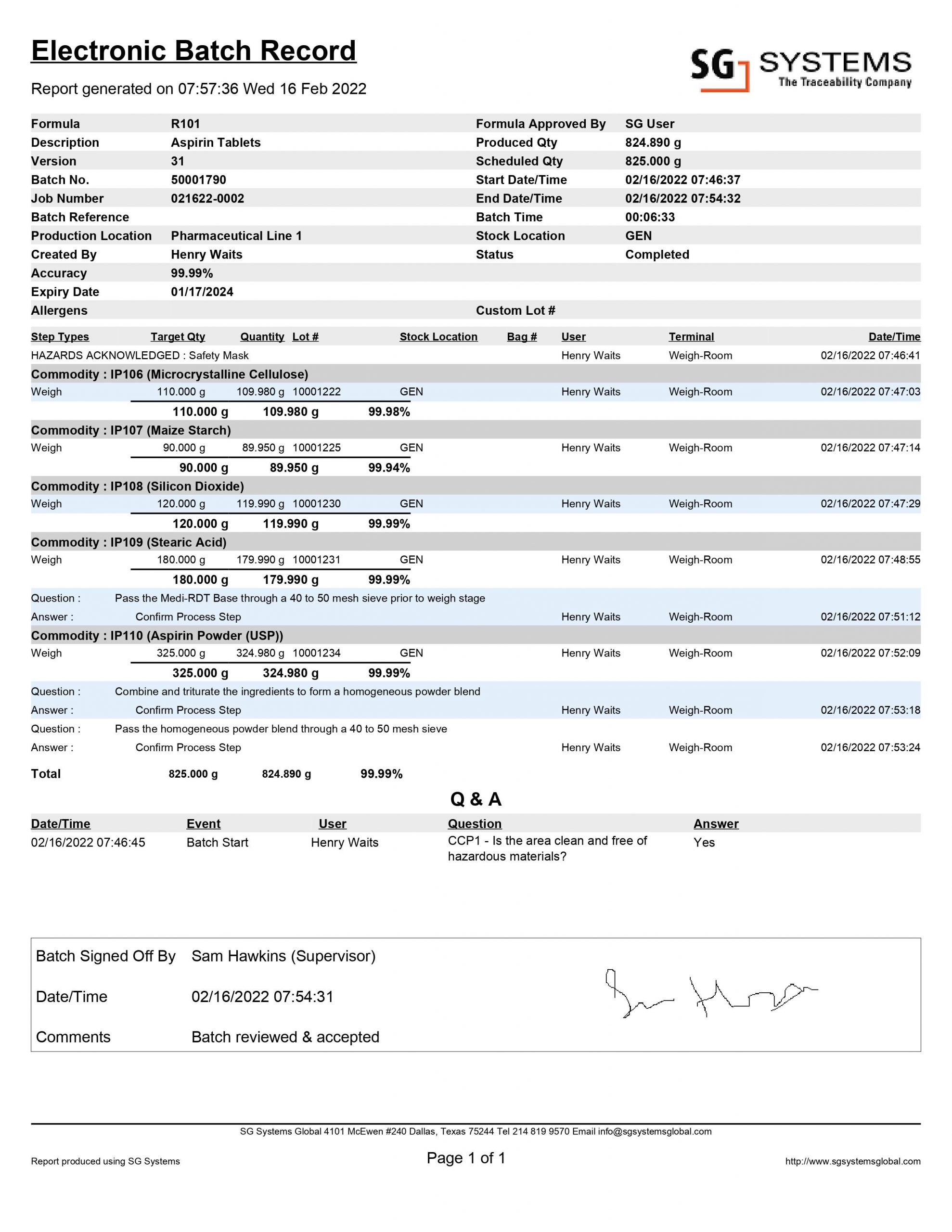
Electronic Batch Records (see sample above) are formally replacing the manual Batch Manufacturing Records with a digital version in compliance with 21 CFR Part 11. EBR’s can take their data from the manufacturing equipment directly (scales and weighing equipment connected to formulation software, barcode scanners for ingredient & lot validation, label printers for human readable WIP batch serialization).
Electronic Batch Record Software
Controlling the electronic batch record processes with V5 Traceability from SG Systems Global, helps manufacturers of all kinds to eliminate human error & remove batch paperwork. Pharmaceutical manufacturers can leverage a system that meets the legislative requirements (providing technical compliance with 21 CFR Part 11) while improving batch consistency and improving quality.
Compliance with ALCOA+ Criteria for Data Integrity
V5 Electronic Batch Record EBR System complies with the original five criteria used for data integrity based on the acronym ALCOA that was developed in the 1980s by an FDA inspector and also with the expanded ALCOA+ from 2010. All of which contribute to the Electronic Batch Record concept.
See the nine-point criteria listed and summarized below:
- Attributable Identification of the individual who performed an activity and the date that they performed. Time is also applicable with a computerized system and time zone if a system spans time zones.
- Legible Can you read and understand the electronic data together with any associated metadata or all written entries on paper? Legible should also extend to any original data that has been changed or modified by an authorized individual so that the original entry is not obscured.
- Contemporaneous Documented (on paper or electronically) at the time of activity.
- Original A written observation or printout, or a certified or verified copy thereof, or an electronic record including all metadata of an activity.
- Accurate No errors in the original observation(s) and no editing without documented amendments/audit trail entries by authorized personnel. Any instrumentation used is qualified and calibrated within acceptance criteria.
- Complete All data from analysis including any data generated before a problem is observed, data generated after repeating part or all of the work or reanalysis performed. For hybrid systems, the paper output must be linked to the underlying electronic records used to produce it.
- Consistent All elements of the GMP record such as the sequence of events are consistent and do not contradict each other. Entries are date (all processes) and time (sometimes paper records and all using a hybrid or electronic systems) stamped in the expected order.
- Enduring Recorded on Authorized media e.g., numbered worksheets for which there is accountability or electronic media that can last throughout the record retention period.
- Available The complete collection of records can be accessed or retrieved for review and audit or inspection over the lifetime of the record.
Computer System Validation
As part of the installation of V5 Traceability, SG Systems Global can provide you with system-specific documentation to address IQ/OQ within a fast timeframe.
Electronic Batch Record FAQ’s
What are Electronic Batch Records (EBR)? Electronic Batch Records are digital versions of traditional manual Batch Manufacturing Records used in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
What is the role of EBR in pharmaceutical manufacturing? EBRs maintain lot and batch traceability and are integral in meeting regulatory standards.
How does an EBR differ from a traditional Batch Manufacturing Record (BMR)? An EBR automates and streamlines the documentation process of a BMR, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
Why is there a need for Electronic Batch Records in the pharmaceutical industry? The complexity and variability in drug manufacturing necessitate more automation and reduced error margins, for which EBRs are essential.
What are the benefits of using Electronic Batch Records? EBRs help eliminate human error, reduce paperwork, improve batch consistency, and ensure quality.
How do EBRs comply with regulatory standards like 21 CFR Part 11? EBR systems are designed to meet legislative requirements, ensuring compliance with standards like 21 CFR Part 11.
What is ALCOA+ and how does it relate to EBRs? ALCOA+ is a set of criteria for data integrity, which EBR systems comply with.
What is involved in the computer system validation for EBRs? Validation involves providing documentation that addresses installation and operational qualifications.
Can EBRs integrate with existing manufacturing equipment? Yes, they can directly integrate with existing equipment, allowing seamless data capture.
What is the impact of EBRs on GMP compliance? EBRs significantly enhance compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices.
How does EBR technology improve traceability in pharmaceutical manufacturing? It digitally captures and stores all relevant batch production data, improving traceability.
Are EBRs required by regulatory authorities? While not explicitly required, they are highly recommended for compliance and traceability.
What are the challenges in implementing EBRs? Challenges include ensuring system compatibility, staff training, and meeting regulatory standards.
How does EBR technology address the variability in drug manufacturing processes? EBRs provide a flexible platform adaptable to different processes and batch sizes.
What is the future outlook for EBRs in pharmaceutical manufacturing? The future outlook is promising due to their efficiency, compliance benefits, and integration capabilities.
Can EBRs be customized for specific pharmaceutical manufacturing needs? Yes, EBR systems are typically customizable.
What kind of training is required for staff to use EBR systems effectively? Training usually involves understanding the software interface and compliance requirements.
How do EBRs ensure data security and confidentiality? EBR systems use robust security features to protect sensitive data.
What impact do EBRs have on production efficiency? They improve production efficiency by automating record-keeping and reducing manual errors, essential for GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice).
Are there any environmental benefits to using EBRs? EBRs contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing the need for paper records.
Further information – for additional information on V5 Traceability and it’s Electronic Batch Record | EBR | Batch Manufacturing Record | BMR | Good Manufacturing Practices | GMP applications, please contact www.sgsystemsglobal.com. For a deep dive into 21 CFR Part 11 and computer systems validation, please visit here
North America
SG Systems LLC
4101 McEwen #240, Dallas TX 75244
Phone: +1 214 819 9570
Contact us here
United Kingdom
SG Systems Europe Ltd
Suite 3 Walton Summit Centre, Green Place, Four Oaks Rd, Preston, PR5 8AY
Phone: +44 (0) 114 349 1480
Contact us here
Australia
Wedderburn
101 Williamson Road, Ingleburn NSW 2565
Phone: +61 2 9426 1800
Contact us here
Europe
SG Traceability Systems Ltd
31-32 Greenmount Office Park, Harolds Cross, Dublin D6, Ireland
Phone: +44 (0) 114 349 1480
Contact us here
Rest assured, we value your privacy and are committed to keeping your data safe. By clicking "Continue with recommended settings," you're giving us permission to use cookies. Of course, you're in control – feel free to adjust your cookie settings anytime in our Privacy Preferences.
