Electronic Batch Record (eBR) – A Complete Guide for Regulated Manufacturing
Electronic Batch Record (eBR) technology is transforming compliance and operational efficiency for regulated manufacturing industries. In pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, food, and medical device sectors, the batch record is more than just documentation—it is the core proof of traceability, product quality, and regulatory adherence. The shift from paper-based records to electronic batch records is accelerating as regulators and auditors increasingly expect real-time, audit-ready digital data.
What Is an Electronic Batch Record?
An electronic batch record is a secure, digital version of the traditional paper batch record. It systematically captures all production and quality events—materials, process steps, equipment, personnel, results—directly from the shop floor. An eBR platform ensures each manufacturing step is executed according to pre-approved instructions and regulatory requirements, with real-time validation and electronic signatures for every action. Learn more about regulatory expectations for electronic records at the FDA’s Guidance for Industry – Part 11 and the EMA Annex 11 Guideline.
- Live data capture from operators, equipment, and devices
- Automated enforcement of manufacturing instructions and SOPs
- Electronic signatures (21 CFR Part 11 compliant)
- Instant deviation detection and escalation for CAPA
- Complete audit trail with time-stamped entries and version control
- Automated and accelerated batch review and release
- Native integration with MES, ERP, and QMS platforms
Paper vs. Electronic Batch Record – Key Differences
Traditional paper batch records—sometimes called Batch Manufacturing Records (BMR) or Batch Production Records (BPR)—are still legal under most GMP frameworks. However, they expose manufacturers to a range of risks, including human error, illegible data, lost paperwork, and delayed review. In contrast, electronic batch record systems deliver real-time control, automation, and defensible compliance.
| Function | Paper Batch Record | Electronic Batch Record |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Manual, handwritten | Digital, validated |
| Audit Trail | Manual, error-prone | Automatic, time-stamped |
| Signatures | Wet ink, easily missed | Electronic, enforced |
| Deviation Handling | Manual, after-the-fact | Live, automated |
| Review Time | Days | Minutes to hours |
Why Are Manufacturers Moving to Electronic Batch Records?
Regulatory frameworks such as 21 CFR Part 11, FDA 21 CFR Part 11, EU Annex 11, and ISO 13485 require manufacturers to implement data integrity, secure audit trails, electronic signatures, and reliable process controls. While paper-based records technically remain valid, most manufacturers find electronic batch record systems essential to achieve true compliance and efficiency—especially under FDA, MHRA, or notified body inspection.
- Reduces data integrity risk and regulatory findings
- Enables rapid batch review and release
- Supports automated integration with enterprise systems
- Provides transparency for management and auditors
- Delivers real-time process visibility and exception management
How Electronic Batch Records Work in Practice
Modern eBR solutions such as V5 from SG Systems Global control the entire batch documentation lifecycle. From raw material weighing and recipe formulation to packaging, quality control, and final release, every action is enforced and captured electronically. Built-in checklists, role-based access, electronic sign-offs, and audit-ready logs ensure all records are complete, compliant, and ready for inspection.
- Batch instructions and SOPs are enforced digitally, with step-by-step prompts
- Materials, equipment, and personnel are verified at each stage
- All process data, checks, and outcomes are time-stamped and stored securely
- Deviations are detected immediately and escalated for CAPA
- Integrated with ERP, QMS, and warehouse management systems
- Compatible with Electronic Device History Record (eDHR) requirements for medical devices
Auditors and inspectors are increasingly expecting electronic batch record systems as a baseline for data integrity, traceability, and compliance across regulated manufacturing.
Are Electronic Batch Records Required by Law?
The use of electronic batch records is not explicitly required by law, but the controls they provide are mandated. Regulations demand evidence of traceability, audit trails, and secure, validated records. Electronic batch record platforms make it feasible to meet these requirements in a practical, reliable way, and are rapidly becoming the global standard for regulated production. For more, see the FDA Warning Letters database for examples of data integrity citations.
Electronic Batch Record – FAQs
- Are electronic batch records secure?
Yes, leading eBR systems provide encryption, user authentication, and tamper-evident audit trails. - Can eBRs be validated?
All eBR software used in GMP production must be validated (IQ/OQ/PQ) to demonstrate fitness for use. - What about hybrid systems?
Hybrid systems (paper plus digital) are discouraged by global regulators due to the risk of gaps, missing data, and data integrity concerns. - Can eBRs integrate with ERP?
Yes, modern electronic batch record solutions like V5 offer integration via APIs and native connectors.
The Bottom Line on Electronic Batch Records
The electronic batch record has become the gold standard for data integrity, efficiency, and compliance in regulated manufacturing. While paper records may still meet basic regulatory requirements, they fall short in terms of risk mitigation, real-time control, and audit-readiness. Electronic batch record systems deliver a single source of truth—improving quality, accelerating release, and providing confidence during every audit or inspection.
See an Example Electronic Batch Record
Below is an example page from a digital Electronic Batch Record. This sample highlights core batch data, signatures, and compliance checkpoints. Please note: this is an excerpt from a much larger, multi-page report typically generated by advanced eBR platforms.
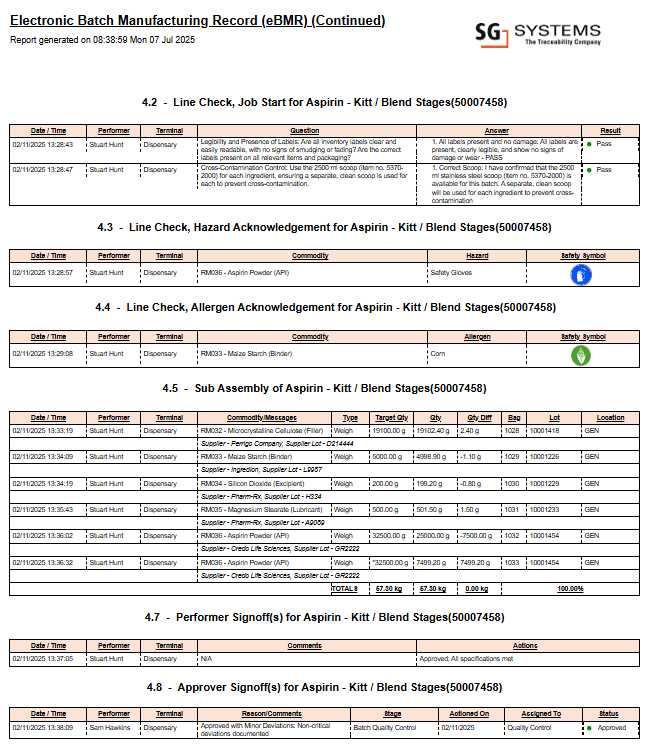
This page is a single example extracted from a comprehensive multi-page electronic batch record generated by leading eBR software solutions.



